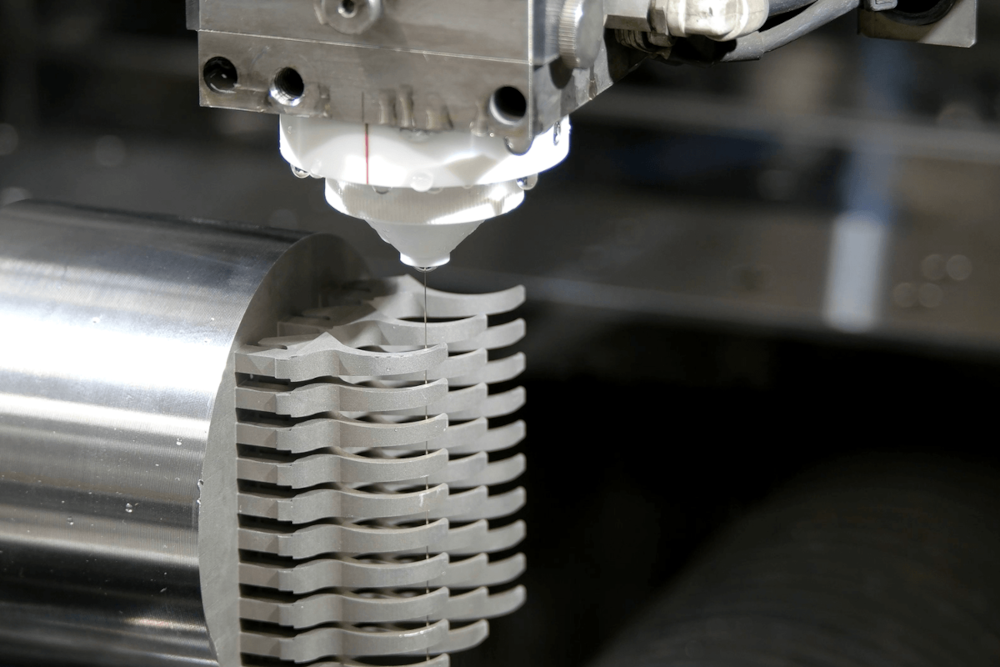
Wire-cut Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) performs at the apex of precision engineering, revolutionizing industries through its intricate cutting and shaping capabilities.
Using a controlled electrical discharge, wire EDM machine tools effortlessly carve intricate shapes from conductive metals with micron-level accuracy. Wire EDM’s non-contact machining process ensures minimal material stress, making it ideal for delicate components.
This exploration of wire EDM production highlights the equipment’s advantages, its machining applications in seven big industries, and its distinguishing features when compared to other machining methods.
How Does Wire EDM Shape Materials into Precise Parts?
First invented by Soviet physicists B. R. Lazarenko and N. I. Lazarenko in the 1940s, EDM has evolved into a sophisticated machining technique. Early iterations of EDM technology, known as “die-sink” or “sinker EDM” machines, were different from the wire EDM technology that emerged later in the 1960s.
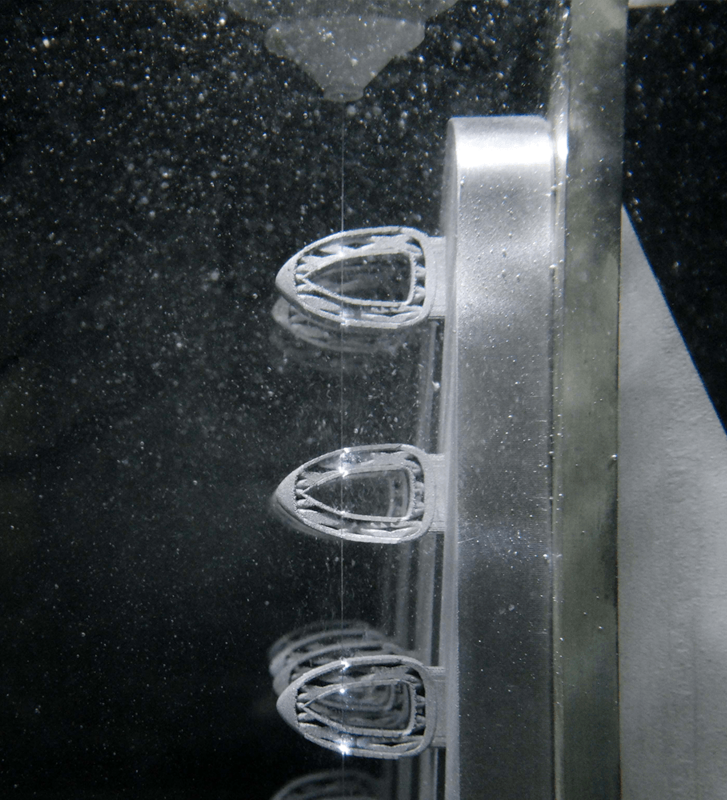
A part being cut by a wire EDM machine while submerged in dielectric liquid
At the heart of the EDM process, wire-cut EDM machines use a thin, electrically conductive wire as an electrode.
The CNC-controlled machinery guides this wire, typically made of brass or similar material, along an engineered path through a workpiece that is submerged in a dielectric liquid.
As the wire approaches the workpiece, a series of high-frequency electric discharges or sparks generated between the wire and the workpiece gradually erode the material to form the designed shape.
How Wire EDM Has Evolved
Advancements in wire EDM technology have ushered in remarkable improvements, enhancing efficiency and versatility for precision manufacturers.
Engineers adjust variables such as wire type, tension, and flushing techniques to optimize wire EDM machinery and meet specific requirements for accuracy and precision.
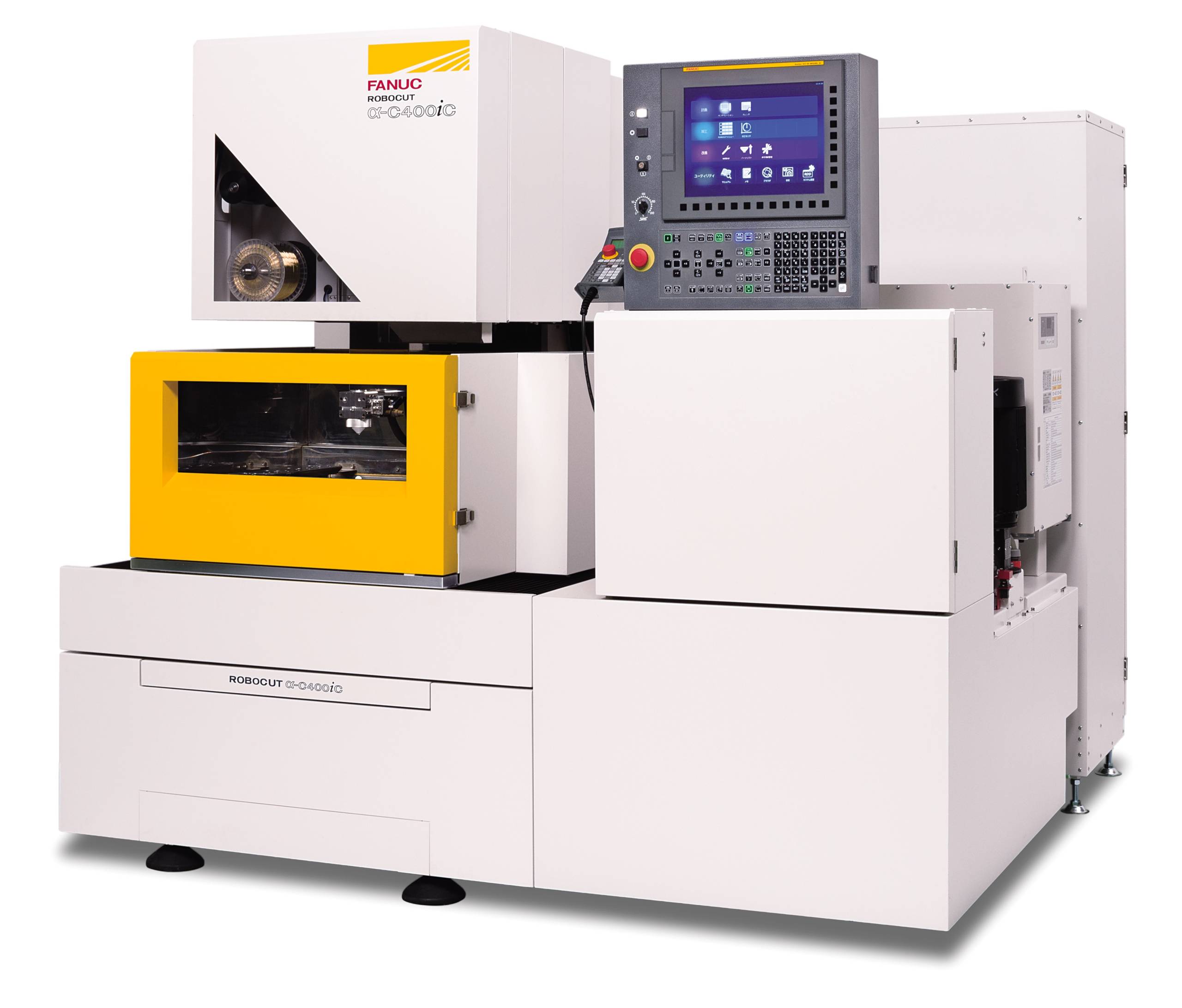

FANUC’s ROBOCUT C400iC Wire EDM
As another example, leading manufacturers of Wire EDM machinery FANUC have introduced revolutionary Automatic Wire Feeder (AWF3) Technology in their ROBOCUT wire EDM machines, which reduces the need for rethreading and increases unattended machining time.
While wire EDM’s mechanism might seem futuristic, its impact on precision manufacturing industries is undeniably real. From aerospace to medical devices, this production method has unlocked new levels of accuracy that were once deemed unattainable for machine shops producing intricate parts.
Advantages of Wire EDM for Manufacturers
The inherent mechanics of wire EDM provide numerous benefits in multiple industries, including:
- Higher precision and accuracy
- Ability to cut complex geometries
- Ability to cut tight radii
- Minimal material waste
- Burr-free finishes
- No direct contact with the workpiece
- Suitable for machining hard materials
- Excellent surface finishing
- Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ) reduction
Limitations of Wire EDM Technology
While wire EDM stands as a testament to precision engineering, it’s essential to acknowledge its limitations in order to form a comprehensive understanding of its capabilities. These limitations, though minor compared to their advantages, offer insights into where alternative machining methods might be more suitable:
- Slow cutting speeds
- Limited material thickness
- Initial setup time and cost
- Wire breakage and threading difficulty
- Recast layer formation
- Workpieces must be conductive material
What Parts or Components are Manufactured Using Wire EDM?
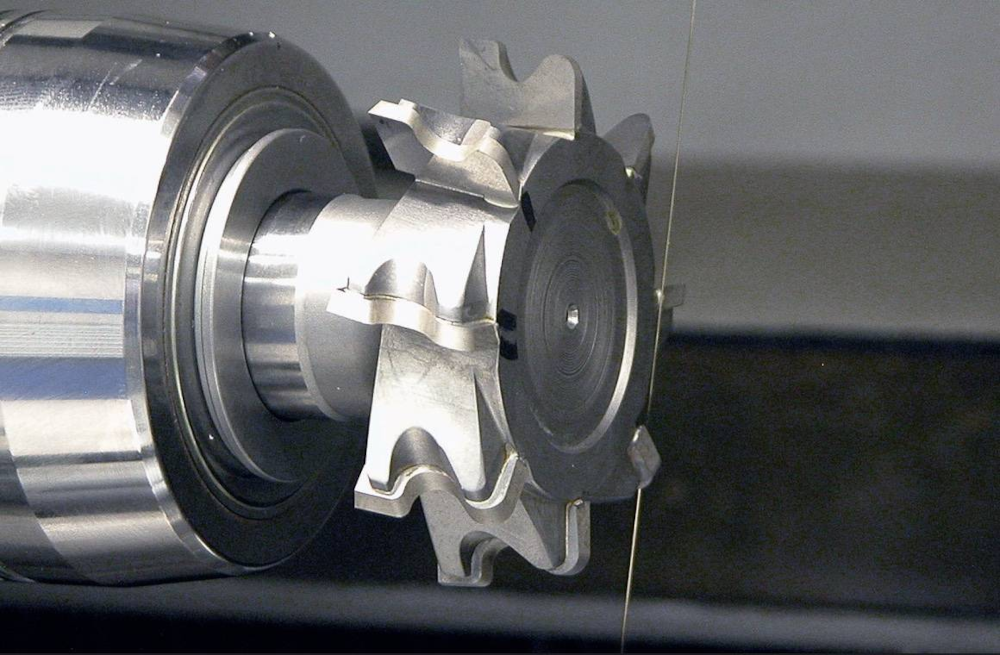 Wire electrical discharge machining offers unmatched versatility when working with various conductive materials, each with unique properties and challenges.
Wire electrical discharge machining offers unmatched versatility when working with various conductive materials, each with unique properties and challenges.
From aerospace components to medical devices, electronics, and automotive parts, industries that demand uncompromising precision are harnessing the advanced capabilities of wire-cut EDM solutions to produce a variety of complex parts, including:
- Turbine blades
- Surgical tools
- Fuel injector components
- Plastic injection molds
- Gemstone settings
- Gears and splines
- Stamping and punching tools
- Medical implants
How Industries are Using Wire EDM
Across diverse sectors, Wire EDM’s capabilities enhance production processes and enable the creation of complex parts. Here are some of its applications across various industries:
Aerospace Industry Applications
In aerospace, precision is paramount for safety and performance, and wire EDM shapes components like turbine blades and engine parts. This guarantees optimal aerodynamics and structural integrity, enhancing aircraft efficiency.
Part/Component |
Common Materials |
|---|---|
| Turbine Blade Roots |
|
| High Precision Fuel Pump CAMS |
|
| Gerotors (Positive Displacement Pumps) |
|
Automotive Industry Applications
Wire EDM proves invaluable for Tier 1 and Tier 2 automotive suppliers fabricating dies, molds, gears, and transmission components. Its precision ensures efficient production, performance, and seamless assembly of critical automotive parts.
Part/Component |
Common Materials |
|---|---|
| Tooling for Automotive Components |
|
| Production PCD and Carbide Tooling |
|
| Wire Crimping Dies |
|
Electronics Industry Applications
Micro-machining and semiconductor manufacturers benefit from the precision of wire EDM technology, as they produce intricate parts like microelectrodes, lead frames, and precise molds that drive advancements in electronics.
Part/Component |
Common Materials |
|---|---|
| PCB Connectors |
|
| Photonics Components |
|
| Semiconductor Components |
|
Tool and Die Making Applications
Wire EDM’s adaptability shines in tool and die production, creating intricate molds, dies, and prototypes. Its precision is essential for achieving complex shapes and maintaining high tolerances.
Part/Component |
Common Materials |
|---|---|
| EDM Sinker Tooling |
|
| Precision Ctamping dies |
|
| Complex Extrusion Dies |
|
Medical Industry Applications
In the medical field, wire EDM crafts surgical instruments, orthopedic implants, and dental tools. Its precision ensures biocompatibility and reliable performance in medical devices.
Part/Component |
Common Materials |
|---|---|
| Surgical Instruments |
|
| Orthopedic Implants |
|
| Orthodontic Ligatures |
|
10 Essential Features Of Wire EDM Machines

Choosing the right wire-cut Electrical Discharge Machining system is a pivotal decision that significantly impacts production quality, efficiency, and versatility.
Evaluate these core features when comparing EDM options:
CNC Control System (Controller)
The CNC control system is the brain behind precision Wire EDM. It dictates movement, coordinates axes, and manages machining parameters. Advanced control systems like those found in Fanuc EDMs, for example, offer intricate programming, seamless integration, and real-time monitoring, ensuring the precise execution of intricate designs.
Wire Diameter and Tensioning Mechanism
Wire diameter influences the precision and intricacy of cuts. A reliable tensioning mechanism ensures consistent wire tension, promoting accuracy and minimizing wire breakage. Machines equipped with automated wire tension control contribute to reliable machining results.
Workpiece Size and Weight Capacity
A machine’s work envelope, determined by its size and weight capacity, influences the dimensions of parts it can accommodate. Machines with larger work envelopes provide the flexibility to manufacture small intricate components and larger parts.
Cutting Speed and Acceleration
Cutting speed and acceleration impact machining efficiency. High cutting speeds and rapid accelerations reduce machining time, enhancing productivity. Look for machines with adjustable parameters to cater to varying material types and complexities.
Automatic Wire Threading
Automatic wire threading is a time-saving feature that streamlines job setups. It minimizes downtime by automatically threading the wire, ensuring uninterrupted production and reducing manual intervention.
Wire Guides and Wire Alignment
Precision Wire EDM relies on accurate wire guides and alignment mechanisms. These features maintain wire trajectory, prevent wandering, and ensure consistent accuracy throughout machining.
Submerged vs. Non-Submerged Machining
The choice between submerged and non-submerged machining impacts machining speed, surface finish, and electrode wear. Submerged machining, where the workpiece is immersed in dielectric fluid, enhances cooling and debris removal.
Dielectric Fluid Filtration and Recycling
Dielectric fluid plays a crucial role in Wire EDM by flushing away eroded material and preventing electrode wear. Machines with advanced filtration and recycling systems extend the fluid’s life, reduce operating costs, and contribute to environmental sustainability.
Automation and Integration Capabilities
Automation and integration capabilities enhance productivity by allowing unattended operation and seamless integration with other manufacturing processes. This feature reduces manual intervention and increases efficiency.
Machine Bed Design and Rigidity
The rigidity of the machine bed ensures stability during machining, translating to higher accuracy and repeatability. A robust machine bed design minimizes vibration and contributes to consistent results.
Get Wire EDM Equipment That Delivers Machining Precision
From aerospace to jewelry design, wire EDM technology has reshaped precision manufacturing, enabling the creation of intricate components that redefine production excellence. Wire EDM equipment continues to push boundaries as machining technology advances, moving towards an innovative future where manufacturing redefines what’s possible with machine engineering and industrial production.